VDC: Versatile Data Cleanser for Detecting Dirty Samples via Visual-Linguistic Inconsistency
Published in The Twelfth International Conference on Learning Representations. ICLR 2024, 2024
Recommended citation: Zhu, Zihao, et al. "VDC: Versatile Data Cleanser for Detecting Dirty Samples via Visual-Linguistic Inconsistency." ICLR 2024. https://arxiv.org/pdf/2309.16211.pdf
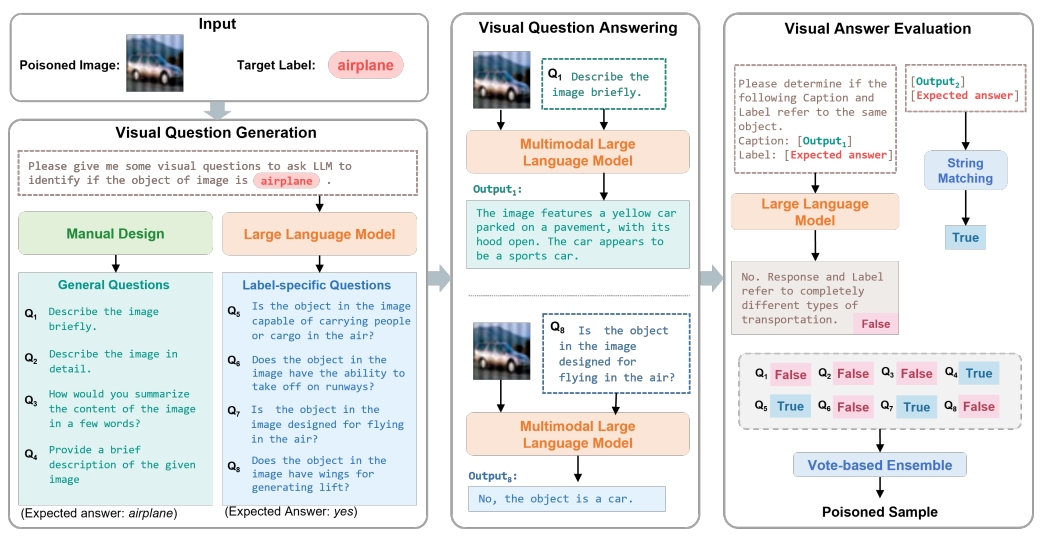
The role of data in building AI systems has recently been emphasized by the emerging concept of data-centric AI. Unfortunately, in the real-world, datasets may contain dirty samples, such as poisoned samples from backdoor attack, noisy labels in crowdsourcing, and even hybrids of them. The presence of such dirty samples makes the DNNs vunerable and unreliable.Hence, it is critical to detect dirty samples to improve the quality and realiability of dataset. Existing detectors only focus on detecting poisoned samples or noisy labels, that are often prone to weak generalization when dealing with dirty samples from other domains.In this paper, we find a commonality of various dirty samples is visual-linguistic inconsistency between images and associated labels. To capture the semantic inconsistency between modalities, we propose versatile data cleanser (VDC) leveraging the surpassing capabilities of multimodal large language models (MLLM) in cross-modal alignment and reasoning.It consists of three consecutive modules: the visual question generation module to generate insightful questions about the image; the visual question answering module to acquire the semantics of the visual content by answering the questions with MLLM; followed by the visual answer evaluation module to evaluate the inconsistency.Extensive experiments demonstrate its superior performance and generalization to various categories and types of dirty samples.